What is Periodontology? Why Is It Important?
Salih ÖNDER2025-04-01T20:43:39+03:00What Is Periodontology and Why Is It Important for Oral Health?
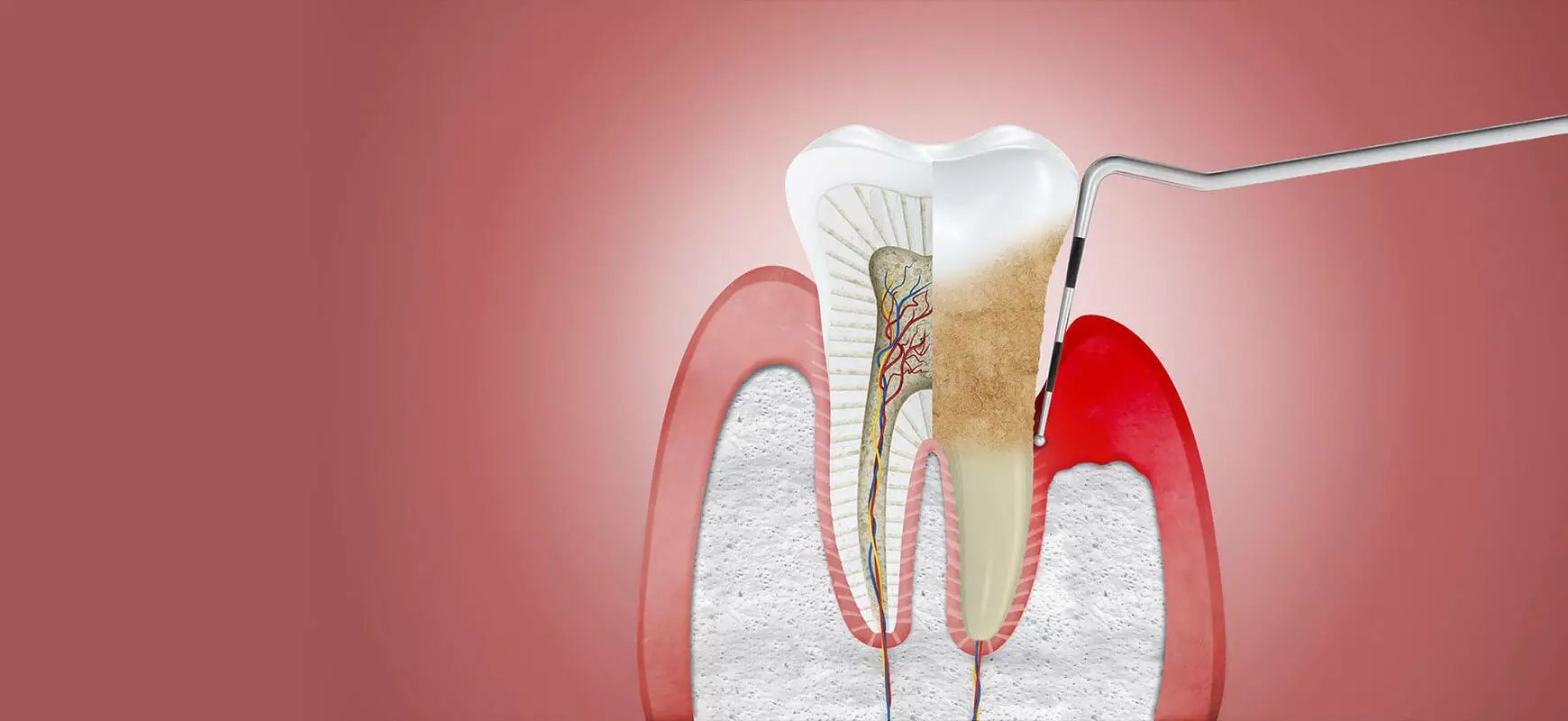
Periodontology is a specialized branch of dentistry that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases affecting the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. This includes the gums, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone.
The importance of it lies in its direct impact on long-term oral health. Healthy gums are essential for keeping teeth firmly in place and preventing conditions such as gingivitis and periodontitis. Without proper periodontal care, patients may experience chronic inflammation, gum recession, and eventually tooth loss. In addition to preserving the teeth, periodontology also plays a role in overall health, as untreated gum disease has been linked to systemic conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
Common Diseases Treated in Periodontology
It addresses a wide range of gum-related conditions. The most commonly treated diseases include:
Gingivitis
The earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums.
Periodontitis
A more advanced form of gum disease where inflammation causes damage to the bone and tissues supporting the teeth.
Gum Recession
The pulling back of the gum tissue from the tooth, exposing the root and increasing sensitivity.
Peri-implantitis
Inflammation around dental implants, similar to periodontitis but affecting implant structures.
Through periodontology, these diseases can be managed or even reversed when diagnosed and treated early.
Early Warning Signs That May Require Periodontology Consultation
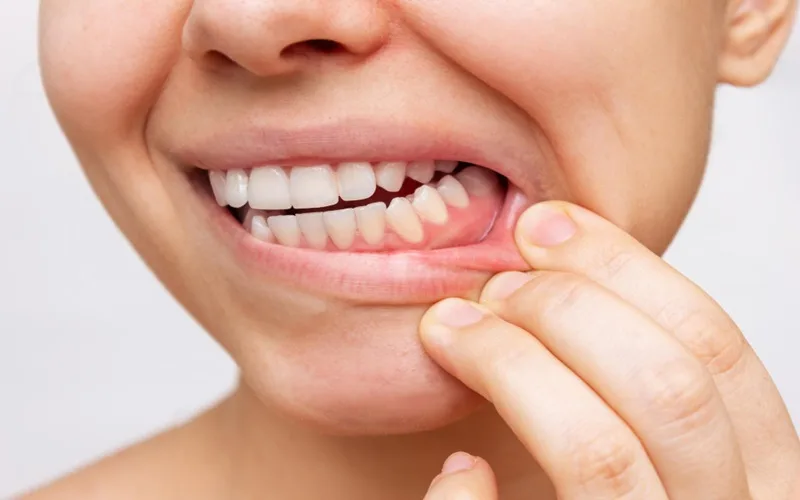
Recognizing the early symptoms of gum disease can prevent serious oral health issues. Patients should consider seeing a periodontology specialist if they experience any of the following:
Gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing
Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
Swollen, red, or tender gums
Receding gums or teeth that appear longer
Loose or shifting teeth
Pain while chewing
These symptoms may indicate underlying gum disease and should not be ignored. Consulting a periodontology expert can help catch issues early and preserve both teeth and gums.
How Periodontology Specialists Diagnose Gum Problems
An evaluation typically begins with a comprehensive oral examination. The specialist will assess the condition of the gums, measure pocket depths around each tooth using a periodontal probe, and check for bleeding, plaque accumulation, and gum recession.
Additional diagnostic tools may include:
Dental X-rays to evaluate bone loss
3D imaging or digital scans for detailed views of the mouth
Periodontal charting to document the health of each tooth’s supporting structures
These diagnostic methods allow periodontology professionals to develop a tailored treatment plan based on the severity of the condition.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options in Periodontology
Not all periodontal issues require surgery. In many cases, it offers effective non-invasive treatments to manage gum disease and prevent further progression.
Common non-surgical procedures include:
Scaling and Root Planing
Deep cleaning below the gumline to remove plaque and tartar buildup
Antibiotic Therapy
Topical or oral antibiotics to reduce infection
Laser Therapy
Minimally invasive treatment to remove diseased tissue and bacteria
Oral Hygiene Instruction
Personalized guidance to improve at-home care routines
These treatments are often the first step in periodontology and can lead to significant improvements in gum health.
Surgical Procedures in Periodontology for Advanced Gum Disease
When non-surgical methods are not sufficient, periodontology provides surgical options to restore gum and bone health. These procedures are usually performed for patients with moderate to severe periodontitis.
Common surgical techniques include:
Flap Surgery
Lifting the gums to clean deeper areas and reduce pocket depth
Bone Grafts
Rebuilding lost bone with natural or synthetic materials
Gum Grafts
Covering exposed roots with healthy tissue to reduce sensitivity and prevent further recession
Guided Tissue Regeneration
Encouraging the growth of new bone and tissue in affected areas
This type of surgery is typically done under local anesthesia and has a high success rate when followed by proper aftercare.
The Role of Periodontology in Preventing Tooth Loss
Tooth loss is often the final stage of untreated gum disease. Periodontology plays a critical role in identifying and treating problems early, before they lead to irreversible damage.
By maintaining the health of the gums and the supporting bone, periodontology helps to:
Stabilize teeth and prevent mobility
Control inflammation and infection
Promote long-term oral stability and function
Reduce the need for tooth extractions or dentures
Through both preventive care and advanced treatment, periodontology supports lifelong oral health and helps patients retain their natural teeth for as long as possible.
Daily Habits That Support Periodontology and Gum Health
Good oral hygiene habits are essential for preventing gum disease and supporting the effectiveness of periodontic treatments. Consistent care at home can greatly reduce the risk of developing issues that lead to periodontal intervention.
Some daily habits that promote gum health include:
Brushing teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush
Using fluoride toothpaste to strengthen tooth enamel
Flossing daily to remove plaque between the teeth and below the gumline
Rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce oral bacteria
Staying hydrated to support saliva production and overall oral hygiene
In addition, regular dental check-ups and cleanings play a vital role in detecting early signs of gum disease and keeping periodontal tissues healthy.
How Periodontology Connects to Your Overall Health
The relationship between gum health and systemic health is well established in medical research. Periodontology not only helps maintain the health of the mouth, but also plays a role in preventing or managing certain chronic conditions.
Scientific studies have linked periodontal disease with:
Cardiovascular disease, due to inflammation and bacterial spread
Diabetes, which both contributes to and is worsened by gum disease
Respiratory infections, where oral bacteria may travel to the lungs
Adverse pregnancy outcomes, including low birth weight and preterm birth
By addressing gum disease through periodontology, patients may also reduce their risk of developing or aggravating these systemic health issues.
Latest Technologies Used in Periodontology Treatments

Modern periodontology has benefited significantly from advancements in dental technology. These innovations make diagnosis more precise and treatment more comfortable and effective.
Some of the latest technologies used in periodontology include:
3D imaging and digital scans for accurate treatment planning
Laser therapy for minimally invasive gum treatments
Computer-guided implant placement for improved outcomes
Regenerative materials that promote natural tissue healing
These tools allow periodontology specialists to deliver personalized care with faster recovery times and longer-lasting results.
It might interest you –> Antalya Dental Clinic
What to Expect During a Visit to a Periodontology Clinic
Visiting a periodontology clinic may feel unfamiliar at first, but the process is straightforward and patient-focused. The goal is to assess gum health and create a customized treatment plan based on individual needs.
A typical visit may include:
A detailed review of your medical and dental history
A full periodontal examination, including probing and imaging
Discussion of findings and recommendations for treatment
Education on oral hygiene practices and preventive strategies
The periodontology team will ensure that you are comfortable and fully informed throughout the process.
Click and learn –> Dental Implants Turkey
Frequently Asked Questions About Periodontology
What Does a Periodontology Specialist Treat?
Periodontology specialists focus on gum disease, gum recession, bone loss, and other issues affecting the structures that support the teeth.
Is Gum Disease Reversible?
In its early stage (gingivitis), gum disease is often reversible with proper care. More advanced cases require ongoing treatment and maintenance through periodontology.
How Often Should I Visit a Periodontist?
This depends on your oral health status. Patients with existing gum disease may need visits every 3–4 months, while others may benefit from annual check-ups.
Is Periodontal Treatment Painful?
Most procedures are done under local anesthesia and are generally well tolerated. Non-surgical treatments cause little discomfort, and surgical options are designed to be as minimally invasive as possible.
Can I Prevent Periodontal Disease?
Yes. Good daily oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and regular dental check-ups are the most effective ways to prevent gum disease and the need for intensive periodontology treatment.
For your information –> Hollywood Smile Turkey
Treatment Summary
Number of Transactions
2-3
Return to Work Process
Now
Processing Time
10 Days
Full Recovery Process
Now
Anesthesia Method
Local anesthesia
Persistence of Results
5 Years
Sensitivity Process
Non
Eating - Drinking Process
2 Hours Later
Note: *The information and recommendations on this page are for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment. WhatsApp line.
Bütün İşimiz Diş